EV & GRID
RAPID CHARGING CHANGES THE ENERGY STORAGE GAME

Carbon-Ion cells have unique properties that allow them to charge and discharge extremely quickly, while still retaining meaningful energy storage, which enables delivery of fast, clean power-on-demand. These unique Carbon-Ion cells deliver a powerful boost in hybrid systems, for example enabling enhanced grid revenue stacking or even powering take-off in electric-powered aviation.

We are in the midst of a transition to fully electric living, which is disrupting nearly every industry on the planet. As a result, there is a critical need for better and more diverse energy storage in order for many industries to provide more impactful solutions to consumers of all kinds. C-Ion is here to bridge this gap in a groundbreaking way by delivering fast, clean power-on-demand to a broad range of applications from infrastructure to individual products, and from grid services to UAVs.

Carbon-Ion’s technology and unique material properties allow an extremely fast response time that adds more value to the entire power system. Carbon-Ion cells are designed to deliver high cycle life and ramping capabilities, along with repeated high cyclic storage with no performance degradation. This creates significant efficiencies in energy systems that will, in turn, save money, time, and resources.
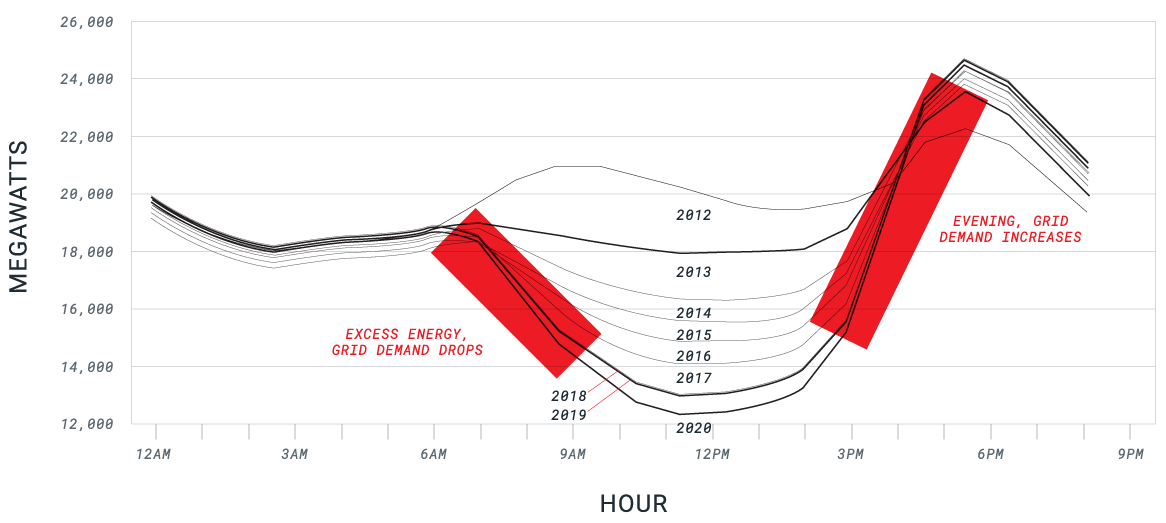
Significant loss of grid inertia has led to more frequency deviations than before, and a range of technologies is needed to plug this gap as we move toward a grid that is fully supplied by sustainable energy generation – this will be true in every country in the world if ‘net-zero’ is adopted.
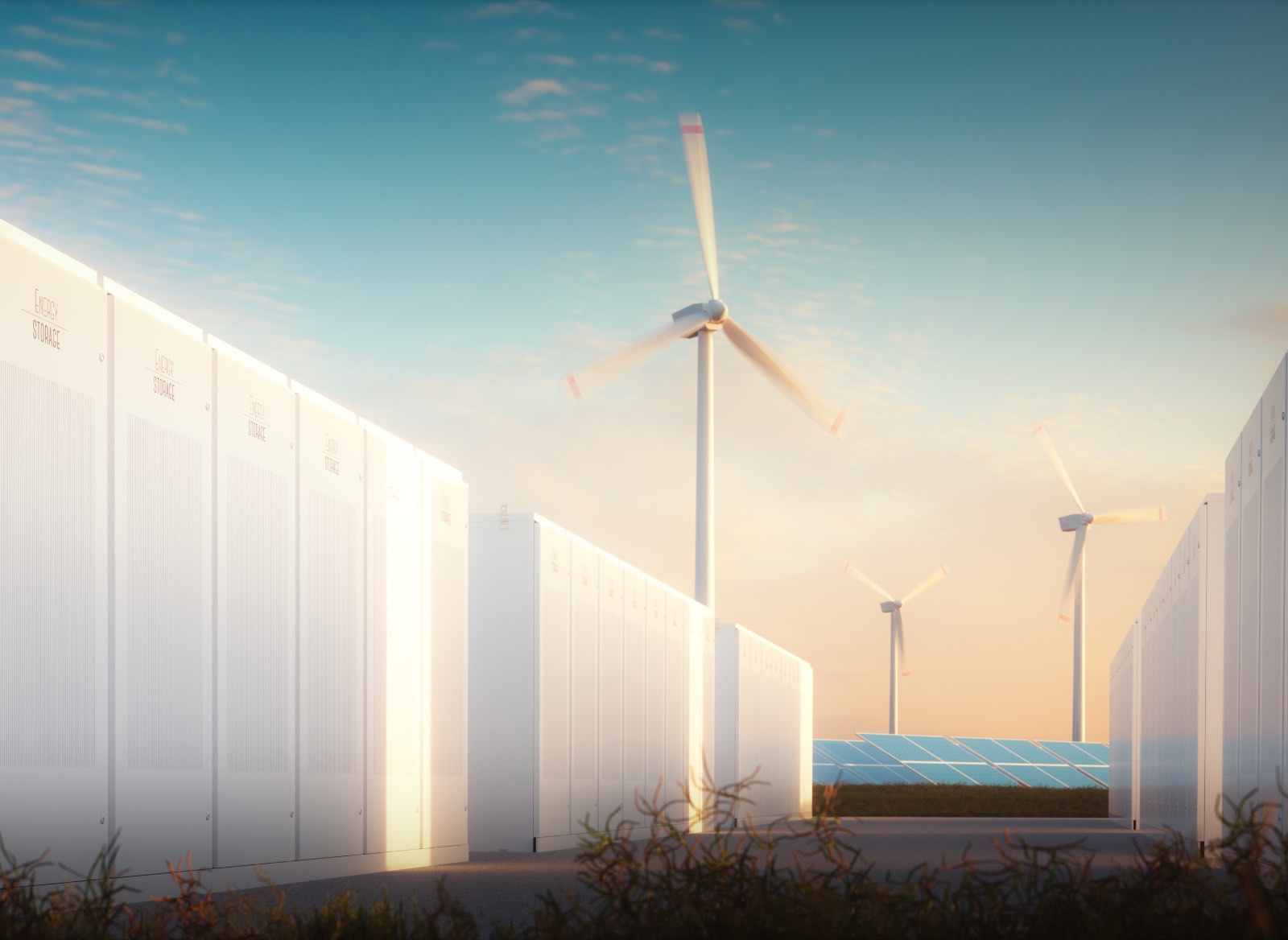

C-Ion can perform several roles. It harnesses the ability to perform fast-responding short-term energy storage to take energy from or provide energy to the grid, and can provide support to improve the round-trip efficiency of renewable energy generation assets.
It can provide lifetime extension of other energy storage assets through hybridization at either system or grid level by providing peak shaving of transient loads on existing energy storage technologies and by bridging the gap between batteries and supercapacitors in aggregated generation, which enables enhanced revenue stacking.
Drivers are used to filling a tank in a gasoline, petrol, or diesel vehicle in 5 minutes and then driving 500 miles or more before they must fill up again. Carbon-Ion believes that drivers will demand the same experience before switching to electric vehicles, and Carbon-Ion’s C-Ion technology could help make this possible.

Bloomberg estimates that the world demand for Lithium-ion batteries could reach 400GWh (Gigawatt hours) by 2025 as demand for electric vehicles grows. At the same time, the mass roll-out of EVs will challenge the national grid infrastructure. One solution is to install energy storage at filling stations that allow buffering of the electrical grid, storing energy at low-power from the grid and delivering it at high power (quickly) to vehicles. Governments have the potential to regulate the EV rechargers at the filling stations and apply the same tax currently applied to gasoline and diesel. This will allow continued funding of road infrastructure.
Helping to make this scenario feasible is the next-generation of EVs that will support Extreme Fast Charging (XFC). This allows charging stations to operate at megawatt rates of charge, according to TransportXtra—10 times faster than the current Tesla superchargers. At these rates, recharging an EV for a 300-mile (450 km) range is possible in just five minutes. C-Ion technology is well suited for upgrading the power output of recharging stations where the grid infrastructure is limited.
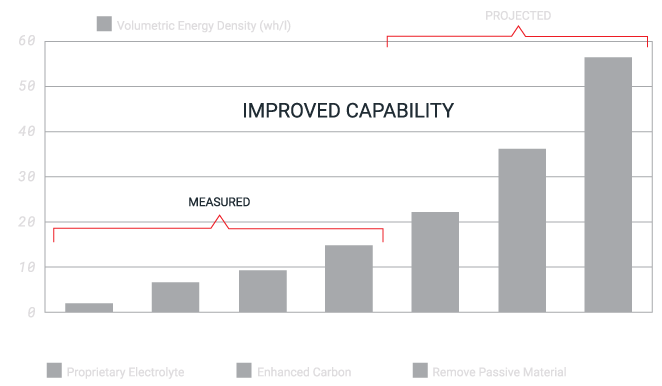
DELIVERABLES 01 2021 – 01 2024
Source: ZapGo Testing and Oxcion Analysis